Certain Windows recovery utilities employ G2LDR (the GRUB2 loader for Windows) to load BOOTMGR from the disk. Normally, this is attempted when the “regular” bootsector used by Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 8 to locate and load BOOTMGR from the boot partition has failed.
- Grldr Missing Windows 7
- Cannot Find Grldr Windows 7
- Grldr.bak Windows 7
- Reparar Grldr Windows 7
- No Grldr Windows 7
For Windows 7 and Vista to pass validation tests and Windows activation, certain codes are added into the boot process thus modifying the BOOTMGR. Once the BOOTMGR refuses to load unsigned Windows kernels, “grldr” is used instead. No Grldr Windows 7. If you made a repair disk you should be able to use that to fix the problem. GRLDR is a nickname/abbreviation for the GRUB bootloader for Windows (also known as Grub4Dos or Grub for Dos), and is often used to set up a PC to dual-boot into Windows and one or more Linux (or other.nix-based) operating systems.
From Grub4Dos Wiki
|
Introduction
What is GRUB for DOS
GRUB for DOS is an universal boot loader based on GNU GRUB. It can boot off DOS/LINUX, or via Windows boot manager/syslinux/lilo, or from MBR/CD. It also has builtin BIOS disk emulation, ATAPI CDROM driver, etc.
Difference between GRUB for DOS and GNU GRUB
First of all, GRUB for DOS has a flexible boot loader. Unlike GNU GRUB which relies on three stages of files to boot, GRUB for DOS uses a much better solution. The main function of GRUB is placed in a single file grldr, while the boot loader is placed in another file grldr.mbr, which can be installed to MBR or partition boot sector. At startup, boot code in grldr.mbr will dynamically scan the root directory of every local partition for grldr, and load the first one found. Using this scheme, the location of boot file is no longer fixed, users can move it across partition boundary without causing booting problems.
Secondly, GRUB for DOS can be loaded in multiple ways. GRUB for DOS runtime image comes in two forms. One is grldr, which can be loaded by MBR/partition boot sector and the Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista boot manager. It can also act as the eltorito boot file for bootable CDROM. The other is grub.exe, which is a hybrid executable that can be launched from linux console and DOS prompt.
Thirdly, GRUB for DOS extends the function of GNU GRUB. The most significant enhancement is the map command. In GRUB for DOS, the map command can be used to create virtual harddisks and floppies from image files. These virtual devices can be accessed even after DOS starts.
There are other useful features of GRUB for DOS which are not present in GNU GRUB, such as ATAPI CDROM driver, Chinese support, and so on.
Installation
There are many ways to install GRUB for DOS. Some of them require modifying MBR or partition boot sector, while others require changing system startup configuration files.
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to MBR
You can use bootlace.com or grubinst.exe to install GRUB for DOS boot code to MBR:
bootlace.com can be used in DOS, Windows 95/98/Me and Linux. Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of first hard drive under DOS, Windows 95/98/Me:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of IDE channel 0, primary drive under Linux:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of hard drive image file aa.dsk:
grubinst.exe can be used in Linux, FreeBSD and Windows NT family OSs (Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista). Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of first hard drive under Windows NT family OSs:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of IDE channel 0, primary drive under Linux/FreeBSD:
You can also use device names:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of hard drive image file aa.dsk:
There are many options you can use with bootlace and grubinst, use the -h option to display help message.
After installing the boot code, you need to copy grldr and menu.lst to the root directory of any FAT16/FAT32/NTFS/EXT2 partition.
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to partition boot sector
You can use grubinst to install GRUB for DOS boot code to partition boot sector. Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the first primary partition of the first hard drive:
or
or
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the first primary partition of the hard drive image file aa.dsk:
or
Just as in GRUB, extended partition starts with (hd0,4).
After installing the boot code, you need to copy grldr and menu.lst to the partition which you install the boot code on.
Starting GRUB for DOS from DOS
You can use load GRUB for DOS in config.sys using one of the following lines:
grub.exe can also be launched from DOS prompt or batch file such as AUTOEXEC.BAT.
Starting GRUB for DOS from Linux
First, you need to apply the kexec patch to the Linux kernel.
Then, you can use the following commands to launch GRUB for DOS from linux:
Booting GRUB for DOS via the Windows NT/2000/XP/2003 boot manager
Add the following line at the end of boot.ini (this file is hidden):
Then copy grldr to C:, and create the GRUB4DOS configuration file at C:menu.lst.
Next time you start windows, there is a new option 'Start GRUB4DOS' which can be used to start GRUB for DOS.
Booting GRUB for DOS via the Windows Vista boot manager
Use bcdedit to configure the startup menu:
Then copy grldr.mbr to C:, grldr and menu.lst to the root directory of any FAT16/FAT32/NTFS/EXT2 partition.
Note: previous version of grldr.mbr can also be used in boot.ini of Windows NT/2000/XP/2003. But it doesn't work anymore with the latest version.
Loading GRUB for DOS using other boot loader
grub.exe can be loaded as a linux kernel.
Load GRUB for DOS using GRUB or another copy of GRUB for DOS, add the following section to menu.lst:
Load GRUB for DOS using syslinux, add the following section to syslinux.cfg:
Booting DOS/Windows 9X/Windows NT startup files
In GRUB for DOS, you can load the DOS/Windows 9X/Windows NT startup files directly.
DOS, Windows 95/98/Me:
Windows NT/2000/XP/2003:
Windows Vista:
Disk emulation
In GRUB for DOS, disk emulation is implemented using the 'map' command.
Direct mapping
Here is an example of mapping a image file as virtual floppy, and boot from it:
map --hook is used to make the mapping created by first map command take effect immediately.
Here is an example of booting from the virtual hard disk:
Map the image file as virtual hard disk, but boot from the original disk:
CDROM emulation is not implemented.
In direct mapping, the image file must be contiguous.
The virtual disk is implemented using INT 13. Therefore, it can be accessed in system that still uses INT 13, such as all kinds of DOS and Windows 9X (compatible mode disk access), and it can't be accessed in system that usesprotected mode drivers, such as Linux, FreeBSD and Windows NT family OSs.
Indirect mapping
Indirect mapping is very similar to direct mapping, here is an example:
The --mem option indicates indirect mapping.
In indirect mapping, the image file is copy to memory before the mapping is applies, therefore, the image file need not to be contiguous, however, you must have enough memory to hole the image file.
Auto MBR creation
To create virtual hard disk, you need an image file that resemble a real hard disk, which consist of MBR and partition data. If the image file only contains partition data, you need to patch it with MBR to create disk image. GRUB for DOS has taken this into consideration. When mapping disk image file, it will test the presence of MBR, if not found, it will create MBR automatically using the partition data. For example:
aa.dsk can be either disk image or partition image, in the later case, GRUB for DOS will create the MBR in the air.
memdisk
The indirect mapping of GRUB for DOS is similar to the function of external tool memdisk from syslinux. In fact, the following two menu entries do roughly the same thing:
However, memdisk does not support direct mapping or auto MBR creation.
CDROM related subjects
Using ATAPI CDROM in GRUB for DOS
Use the following command to initialize ATAPI CDROM:
Then, use the following command to start using ATATPI CDROM:
After cdrom --hook, the CDROM device can be accessed using (cd0), (cd1), etc.
To boot from the first CDROM, use the following commands:
To stop using CDROM:
The first command removes the (cdN) device mapping, while the second one stops the CDROM driver.
Note: If you boot GRUB for DOS from CDROM, the booting device will be (cd). This device is always accessible. However, if you want to access file from other CDROMs, you still need to initialize them using the above commands.
Examples:
To boot from the first CDROM:
Create a bootable CDROM
In GRUB for DOS, you can use grldr to create bootable CDROM:
grldr and menu.lst should be placed at the root directory of CDROM image.
The above two commands can both create a bootable CDROM, but they are not totally the same.
Grldr Missing Windows 7
The first one tells BIOS to load the whole grldr. However, some buggy BIOS might ignore it and load only a portion of the file, typically one sector (2048 bytes). This will cause the program to fail.
The second one tells BIOS to load only the first sector (2048 bytes), and the program loads the rest from CDROM. This method is safer, it should work for most BIOS.
Note: you can optionally use the -boot-info-table option, but the info table will be ignored by the program.
Load GRUB for DOS from BCDW
To load GRUB for DOS from BCDW, first copy grldr and menu.lst to the root directory of CDROM image, then add a new line to the [MenuItems] section of BCDW configuration file bcdw.ini:
No booting error should stop you from using your computer or laptop. “No grldr” error message is no exception. This issue is common among Linux and Ubuntu users. In this guide, we’ve listed and illustrated the easiest common solutions that will help you fix the “no grldr” error. Also included is a brief on what is .grldr, symptoms, and causes of the error.
Part 1: Symptoms No GRLDR Error
Grldr file Is also termed as the GRUB bootloader. Its function is to maintain the internal load data for the GRUB4DOS. The GRUB4DOS is a universal bootloader that offers PC users the chance to dual-boot into Windows and Linux operating systems.
If you did an iso installation and the PC shut down while still installing updates, the next time you reboot it, you’ll likely get the error No GRLDR. The screenshot below shows how the error looks like.
This error appears in different versions. Below are two examples:
Example 1: The error appearing on the PC when you boot is “Cannot find GRLDR.”
Example 2: This error message has slightly more additional tests compared with the first screenshot.
Part 2: Causes of No GRLDR Error
The dual-boot challenge in Linux can be said to be the main reason for this error. But we can’t limit ourselves to this challenge only. The reason being the booting process is a complex process that involves the configuration of many files, software, and data.
The causes discussed below will help you in knowing which solution to implement.
Cause 1: Incorrectly updated NTFS bootsector
If your computer is allowed to do automatic updates, certain third-party software will do unauthorized updates, upgrade utilities, reconfigure some data and at times repair FAT32 or NTFS bootsector. When these changes are made in your computer, the boot chain is broken and thus causing the “no GRLDR” error to appear.
Cause 2: Failed Linux installation
Cannot Find Grldr Windows 7
Cause 3: Creation of Windows activation bypass
For Windows 7 and Vista to pass validation tests and Windows activation, certain codes are added into the boot process thus modifying the BOOTMGR. Once the BOOTMGR refuses to load unsigned Windows kernels, “grldr” is used instead. When the patched GRLDR files can no longer load, the “No GRLDR” error will appear on your screen.
Part 3: Solutions to “No GRLDR” Error
This part deals with how to fix “No GRLDR” Error. Most of the solutions below require free installation CDs. They are therefore easy to follow. For Windows 10, you can try the solutions provided by Wondershare Recoverit.
Grldr.bak Windows 7
Solution 1: Rebuild BOOT.ini
There are two options for this solution.
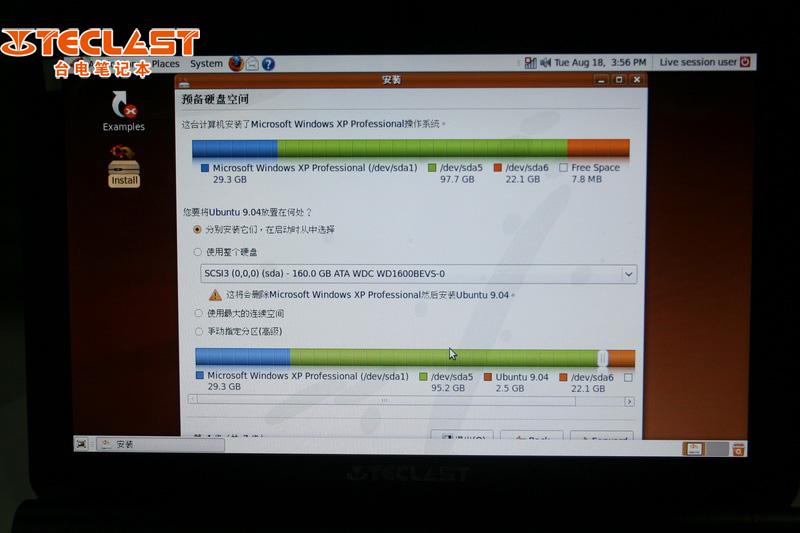
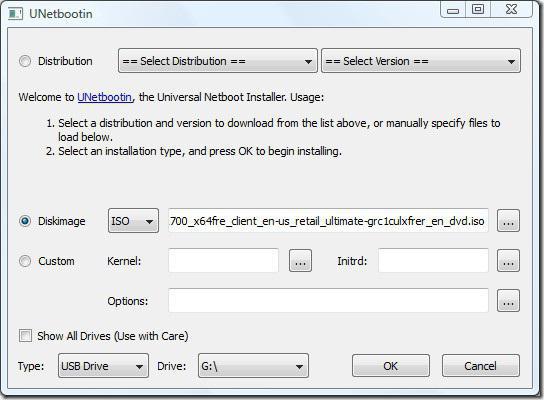
You can either create a boot repair disk and boot on it or do a boot-repair installation in Ubuntu. When repairing the boot.ini from a created disk, install the ISO via a Universal USB Installer, UnetBootin, or LiliUSB.
If you want to install Boot-Repair, boot your computer from an Ubuntu live-CD and then select “Try Ubuntu”. Connect your Linux to the internet, type the commands below, and press Enter after each command.
Option 2: Rebuild the Windows boot.ini using Microsoft CD
Step 1: Insert Microsoft Windows XP CD into your computer and press any key to reboot from the CD.
Reparar Grldr Windows 7
Step 2: In the prompt Microsoft Setup Menu, hit the “R” button to launch the Recovery console.
Step 3: Choose the operating system to use
Step 4: If prompted to enter a password, type the Admin password and hit Enter
Step 5: Type bootcfg /rebuild in the prompt command to begin the rebuild process and press Enter
Step 6: Press “Y” in the next prompt command to identify the installed operating systems on your computer. This is only available to Windows XP users.
Step 7: Next, type /fastdetect and wait for the system to detect the available load options
Step 8: Type Exit to reboot your computer.
This solution should solve the “no GRLDR” error if your computer is running from Windows XP if the boot.ini and MBR/bootsector are repaired successfully.
Solution 2: Use Startup Repair to rebuild BCD and bootsector
Startup Repair is a free-to-use repair tool found in the Windows setup disc that automatically diagnosis and repairs issues in the PCs operating systems.
Step 1: Insert Windows installation DVD to the PC’s CD-ROM drive,
Step 2: Shut down your computer and wait to ensure it’s fully powered down.
Step 3: Start the computer, wait for the “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD…” prompt and press any key-Say F6.
Step 4: Select language and keyboard options. Next click “Repair your computer.”
Step 5: Give your PC some seconds to scan for Windows installations and select the installed system.
Step 6: From the suggested recovery options, select “Startup Repair” to start scanning and repairing errors on your computer.
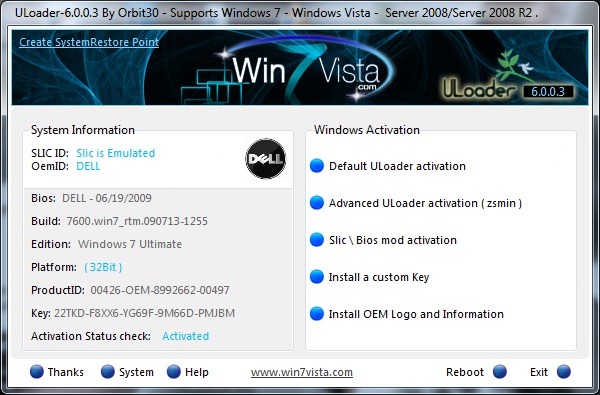
Solution 3: Enquire for a valid Windows 7/ Vista license
If your error occurred due to the creation of an activation bypass on the installed operating system, obtaining the necessary license would help fix “No GRDLR” error.
Go to the Microsoft website to obtain a valid license for Windows 7/Vista.
No Grldr Windows 7
Solution 4: Reconfigure Linux entries

Use keywords like “Windows recovery tools” and select the most suitable from the ones suggested.
Conclusion
How to fix “No GRDLR” error shouldn’t appear on your screen if you follow the solutions listed above. It’s a common startup error. For this to be real, you need to know your operating system and the symptoms of the error. Always read the error message first. This will help you guess the cause of any error appearing on your blue screen.
